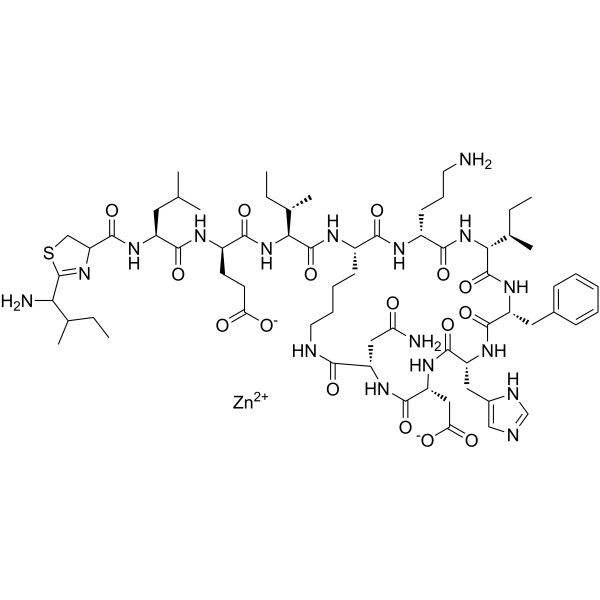
Bacitracin Zinc CAS 1405-89-6 Potency ≥70 IU/mg Peptide Antibiotic Factory
Shanghai Ruifu Chemical Co., Ltd. is the leading manufacturer and supplier of Bacitracin Zinc (Zinc Bacitracin) (CAS: 1405-89-6) with high quality. We can provide COA, worldwide delivery, small and bulk quantities available. If you are interested in Bacitracin Zinc (Zinc Bacitracin), Please contact: alvin@ruifuchem.com
| Chemical Name | Bacitracin Zinc |
| Synonyms | Bacitracin Zinc Salt; Zinc Bacitracin |
| Stock Status | In Stock, Production Capacity 10 Tons per Year |
| CAS Number | 1405-89-6 |
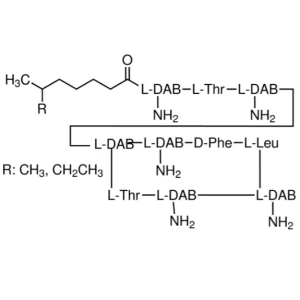
| Molecular Formula | C66H101N17O16SZn |
| Molecular Weight | 1486.07 |
| Melting Point | 250℃(dec.) |
| Water Solubility | 5.1 g/L |
| COA & MSDS | Available |
| Sample | Available |
| Brand | Ruifu Chemical |
| Items | Specifications | Results |
| Appearance | White or Light Yellow-Gray or Beige Powder | Conforms |
| Identification | Meet the Requirements | Appear Positive Reaction |
| pH | 6.0~7.5 | 7.1 |
| Loss on Drying | ≤5.0% | 2.7% |
| Zinc ( Dried Substance) | 4.0%~6.0% | 4.20% |
| Potency | ≥70 IU/mg Microbial Assay (Dried Basis) | 71 IU/mg |
| Content of Bacitracin A | ≥40.0% | 58.2% |
| Content of Active Bacitracin | ≥70.0% (Bacitracin A, B1, B2, and B3) | 86.1% |
| Limit of Early Eluting Peptides | ≤20.0% | 7.6% |
| Limit of Bacitracin F | ≤6.0% | 1.1% |
| Total Viable Aerobic Count | <100 CFU/gram | Conforms |
| Conclusion | The Product Conforms to USP44 Standards | |
| Main Usage | Peptide Antibiotic | |
Package: Bottle, Aluminium foil bag, 25kg/Cardboard Drum, or according to customer's requirement.
Storage Condition: Keep the container tightly closed and store in a cool, dry (2~8℃) and well-ventilated warehouse away from incompatible substances. Protect from light and moisture.
Shipping: Deliver to worldwide by air, by FedEx / DHL Express. Provide fast and reliable delivery.
Bacitracins, zinc complex.
Bacitracins zinc complex [1405-89-6].
» Bacitracin Zinc is the zinc complex of bacitracin, which consists of a mixture of antimicrobial polypeptides, the main components being bacitracins A, B1, B2, and B3. It has a potency of not less than 65 Bacitracin Units per mg, calculated on the dried basis. It contains not less than 4.0 percent and not more than 6.0 percent of zinc (Zn), calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage- Preserve in tight containers, and store in a cool place.
Labeling-Label it to indicate that it is to be used in the manufacture of nonparenteral drugs only. Where it is packaged for prescription compounding, label it to indicate that it is not sterile and that the potency cannot be assured for longer than 60 days after opening, and to state the number of Bacitracin Units per milligram. Where it is intended for use in preparing sterile dosage forms, the label states that it is sterile or must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of sterile dosage forms.
USP Reference standards <11>-
USP Bacitracin Zinc RS
Identification-
A: Thin-Layer Chromatographic Identification Test <201BNP>: meets the requirements.
B: It meets the requirements of the liquid chromatographic procedure in the test for Composition.
Sterility <71>-Where the label states that it is sterile, it meets the requirements when tested as directed for Membrane Filtration under Test for Sterility of the Product to be Examined, except to use Fluid A to each L of which has been added 20 g of edetate disodium.
pH <791>: between 6.0 and 7.5, in a (saturated) solution containing approximately 100 mg per mL.
Loss on drying <731>-Dry about 100 mg in a capillary-stoppered bottle in vacuum at 60 for 3 hours: it loses not more than 5.0% of its weight.
Zinc content- [note-The Standard preparations and the Test preparation may be quantitatively diluted with 0.001 N hydrochloric acid, if necessary, to obtain solutions of suitable concentrations, adaptable to the linear or working range of the instrument. ]
Standard preparations-Transfer 3.11 g of zinc oxide, accurately weighed, to a 250-mL volumetric flask, add 80 mL of 1 N hydrochloric acid, warm to dissolve, cool, dilute with water to volume, and mix. This solution contains 10 mg of zinc per mL. Further dilute this solution with 0.001 N hydrochloric acid to obtain Standard preparations containing 0.5, 1.5, and 2.5 µg of zinc per mL, respectively.
Test preparation-Transfer about 200 mg of Bacitracin Zinc, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Dissolve in 0.01 N hydrochloric acid, dilute with the same solvent to volume, and mix. Pipet 2 mL of this solution into a 200-mL volumetric flask, dilute with 0.001 N hydrochloric acid to volume, and mix.
Procedure-Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the Standard preparations and the Test preparation at the zinc resonance line of 213.8 nm, with a suitable atomic absorption spectrophotometer (see Spectrophotometry and Light-scattering <851>), equipped with a zinc hollow-cathode lamp and an air–acetylene flame, using 0.001 N hydrochloric acid as the blank. Plot the absorbances of the Standard preparations versus concentration, in µg per mL, of zinc, and draw the straight line best fitting the three plotted points. From the graph so obtained, determine the concentration, in µg per mL, of zinc in the Test preparation. Calculate the content of zinc, in percent, in the portion of Bacitracin Zinc taken by the formula:
1000C / W
in which C is the concentration in µg per mL, of zinc in the Test preparation; and W is the weight, in mg, of the portion of Bacitracin Zinc taken.
Composition-
Buffer- Dissolve 34.8 g of potassium phosphate, dibasic, in 1 L of water. Adjust with 27.2 g of potassium phosphate, monobasic, dissolved in 1 L of water, to a pH of 6.0.
Mobile Phase-Prepare a mixture of methanol, water, Buffer, and acetonitrile (26:15:5:2). Mix well, and degas.
Diluent-Dissolve 40 g of edetate disodium in 1 L of water. Adjust with dilute sodium hydroxide to a pH of 7.0.
System suitability solution-Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Bacitracin Zinc RS in Diluent to obtain a solution with a nominal concentration of about 2.0 mg per mL.
Reporting threshold solution-Dilute quantitatively, with water, a suitable volume of System suitability solution to obtain a solution with a known concentration of 0.01 mg per mL.
Peak identification solution-Dissolve a weighed quantity of USP Bacitracin Zinc RS in a suitable volume of Diluent to obtain a solution with a nominal concentration of about 2.0 mg per mL. Heat in boiling water bath for 30 minutes. Cool to room temperature.
Test solution-Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of Bacitracin Zinc in Diluent to obtain a solution with a nominal concentration of about 2.0 mg per mL.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography <621>)-The liquid chromatograph is equipped with an absorbance detector and an end-capped 4.6- × 250-mm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is 1.0 mL per minute. Set the wavelength of the detector at 300 nm. Inject about 100 µL of the Peak identification solution, and identify the location of bacitracin F, which is a known impurity, using the relative retention time shown in Table 1.
Table 1
Component Name Relative Retention Time (approximate)
Bacitracin C1 0.5
Bacitracin C2 0.6
Bacitracin C3 0.6
Bacitracin B1 0.7
Bacitracin B2 0.7
Bacitracin B3 0.8
Bacitracin A 1.0
Bacitracin F 2.4
Change the wavelength of the detector and set it to 254 nm. Chromatograph the System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: identify the peaks of the most active components of bacitracin (bacitracins A, B1, B2 and B3), early eluting peptides (those eluting before the peak due to bacitracin B1) and the impurity, bacitracin F, using the relative retention time values given in Table 1. Calculate the peak-to-valley ratio using the formula:
Hp / HV
in which Hp is the height above the baseline of the peak due to bacitracin B1; and HV is the height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating the bacitracin B1 peak from the peak due to bacitracin B2. The peak-to-valley ratio is not less than 1.2.
Procedure-Separately inject equal volumes (100 µL) of Diluent, Test solution, and Reporting threshold solution. Record the chromatograms for about three times the retention time of bacitracin A. Identify the peaks using the relative retention times shown in Table 1. Measure the peak areas of all peaks in the Test solution. [note-Disregard any peak in the Test solution having an area less than the area of the bacitracin A peak in the Reporting threshold solution; disregard any peak observed in the Diluent.]
note-Total area in the following calculations is defined as the area of all peaks except the reporting threshold.
content of bacitracin a-Calculate the percentage of bacitracin A using the formula:
(rA / Total area) × 100
in which rA is the area response from bacitracin A. Bacitracin A content is not less than 40.0% of the Total area.
content of active bacitracin-Calculate the percentage of active bacitracin (bacitracin A, B1, B2, and B3) using the formula:
(rA + rB1 + rB2 + rB3 / Total area)×100
in which rA, rB1, rB2, and rB3 are the area responses from bacitracin A, B1, B2, and B3, respectively. The sum of bacitracin A, B1, B2, and B3 is not less than 70.0% of the Total area.
limit of early eluting peptides-Calculate the percentage of all peaks eluting before the peak due to bacitracin B1 using the formula:
(rPreB1 / Total area) ×100
in which rPreB1 is the sum of the responses of all peaks eluting before the peak for bacitracin B1. The limit of early eluting peptides (those eluting before the peak due to bacitracin B1) is not more than 20.0%.
limit of bacitracin f- Calculate the percentage of bacitracin F using the formula:
100 × (rF / rA)
in which rF is the response of bacitracin F from the Test solution; and rA is the response of bacitracin A from the Test solution. The limit of bacitracin F, a known impurity, is not more than 6.0%.
Assay-Proceed with Bacitracin Zinc as directed under Antibiotics-Microbial Assays 81.
How to Purchase? Please contact Dr. Alvin Huang: sales@ruifuchem.com or alvin@ruifuchem.com
15 Years Experience? We have more than 15 years of experience in the manufacture and export of a wide range of high quality pharmaceutical intermediates or fine chemicals.
Main Markets? Sell to domestic market, North America, Europe, India, Korea, Japanese, Australia, etc.
Advantages? Superior quality, affordable price, professional services and technical support, fast delivery.
Quality Assurance? Strict quality control system. Professional equipment for analysis include NMR, LC-MS, GC, HPLC, ICP-MS, UV, IR, OR, K.F, ROI, LOD, MP, Clarity, Solubility, Microbial limit test, etc.
Samples? Most products provide free samples for quality evaluation, shipping cost should be paid by customers.
Factory Audit? Factory audit welcome. Please make an appointment in advance.
MOQ? No MOQ. Small order is acceptable.
Delivery Time? If within stock, three days delivery guaranteed.
Transportation? By Express (FedEx, DHL), by Air, by Sea.
Documents? After sales service: COA, MOA, ROS, MSDS, etc. can be provided.
Custom Synthesis? Can provide custom synthesis services to best fit your research needs.
Payment Terms? Proforma invoice will be sent first after confirmation of order, enclosed our bank information. Payment by T/T (Telex Transfer), PayPal, Western Union, etc.
Safety Description S22 - Do not breathe dust.
S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes.
WGK Germany 3
FLUKA BRAND F CODES 3
HS Code 2941909099
Bacitracin is extracted from the culture solution of lichen (Bacillus licheniformis) and is a polypeptide antibiotic. White or light yellow powder, odorless or slightly smelly, bitter taste, hygroscopic. Easily soluble in water and ethanol, unstable, aqueous solution is easily inactivated at room temperature, unstable at pH 9, and should be refrigerated in the refrigerator after dissolution. This product is calculated as a dry product, and the titer per milligram shall not be less than 55 bacitracin units. Bacitracin zinc is bacitracin zinc salt, which is more stable than bacitracin. It is used as a feed additive and has the functions of promoting the growth and development of livestock and poultry, preventing intestinal infections, and increasing feed remuneration. The dosage is the same as bacitracin. Bacitracin antibacterial spectrum is similar to penicillin, which has strong antibacterial effect on gram-positive bacteria and no obvious effect on gram-negative bacteria. For severe infections of drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Oral administration is not absorbed and is used for intestinal infection. External use is also effective for body surface, oral and eye infections and mastitis caused by sensitive bacteria. Has a damaging effect on the kidneys. Bacitracin zinc has been used as a feed drug additive. Oral administration is hardly absorbed, so it is generally believed that there is no drug residue problem in livestock and poultry products. This product is a narrow-spectrum antibiotic, which has a strong antibacterial effect on most gram-positive bacteria. It is also effective against spirochetes and actinomycetes, but it is ineffective against gram-negative bacteria. It has a synergistic effect with a variety of antibiotics such as penicillin G, streptomycin, neomycin, polymyxin, etc. Its zinc salt is mainly used as a feed additive, which has the functions of preventing intestinal infection, promoting growth and improving feed remuneration. Bacteria can slowly develop resistance to this product, but there is no cross-resistance between this product and other antibiotics. This product is highly toxic and cannot be injected. It can be taken orally to treat bacterial diarrhea in livestock and Treponema dysentery in pigs. Clinically, it is often used in combination with a variety of antibiotics such as penicillin, streptomycin, neomycin, polymyxin B, etc. to enhance the efficacy.
Bacitracin Zinc is a complex formed by bacitracin and zinc ions. it is a polypeptide antibiotic and is the most widely used antibiotic feed additive at present. the zinc content is generally 2% ~ 12%. Synthetic products are white or yellowish powder, with special odor, easy to dissolve into weakly alkaline substances, and easily soluble in water, methanol and ethanol. Bacitracin zinc has a strong antibacterial effect against Gram-positive bacteria, and also has antibacterial properties against some Gram-negative bacteria. The use of bacitracin zinc in pig full-price feed can promote growth rate, improve feed remuneration, and prevent pig bacterial diarrhea and chronic respiratory diseases. The addition concentration is generally 10~100mg/kg, and the effect is not significantly improved beyond the addition range. Bacitracin Zinc is generally not absorbed in pig intestines, so there is no residue problem. It is a safe and reliable antibiotic additive. Bacitracin Zinc is highly toxic and is not easily absorbed by the intestine, so it cannot be used as a treatment for systemic infections.
Polypeptide antibiotics have strong antibacterial effect on gram-positive bacteria, and also have antibacterial effect on a few gram-negative bacteria, spirochetes, actinomycetes and even penicillin-resistant staphylococci. The antibacterial mechanism is to inhibit the formation of bacterial cell wall and damage the bacterial cell plasma membrane. It can promote the growth of beneficial microorganisms in the intestine, increase the permeability of the intestinal mucosa, and promote the absorption of nutrients. It is mainly used to promote the growth of livestock and poultry, prevent and control bacterial diarrhea of livestock and poultry and blood dysentery caused by Treponema. Bacitracin zinc is hardly absorbed internally, and most of it is excreted with feces within 2 days, so it is not easy to remain in livestock and poultry products; bacteria rarely develop resistance to bacitracin, and have no cross-resistance with other antibiotics, And has a synergistic effect with penicillin, streptomycin, neomycin, aureomycin, polymyxin, etc. This product is highly toxic and cannot be injected. This product is contraindicated with olaquindox, kitasamycin, virginiamycin, and Enramycin.
As a feed additive, it is mainly used to promote the growth of livestock and poultry, prevent bacterial diarrhea of livestock and poultry and blood dysentery caused by treponema. Bacitracin zinc is hardly absorbed internally, and most of it is excreted with feces within 2 days, so it is not easy to remain in livestock and poultry products; bacteria rarely develop resistance to bacitracin, and have no cross-resistance with other antibiotics, And has a synergistic effect with penicillin, streptomycin, neomycin, aureomycin, polymyxin, etc. This product is highly toxic and cannot be injected. This product is contraindicated with olaquindox, kitasamycin, virginiamycin, and Enramycin.
Bacitracin Zinc is a polypeptide antibiotic, which has a bactericidal effect on gram-positive bacteria. Its mechanism is mainly to inhibit the bacterial wall synthesis of bacteria, and can also combine with the cell membrane of sensitive bacteria, damage the integrity of the cell membrane, and cause The outflow of important substances in the cell. Effectively inhibit Gram-positive bacteria and some Gram-negative bacteria; the rate of bacterial resistance to bacitracin zinc is slow, and there is no cross-resistance with other antibiotics. polypeptide antibiotics inhibit dephosphorylation of lipid pyrophosphate, thus inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial cell walls.